Basic git commands for beginners with examples
Git is a popular version control system (VCS). Wait , what is a Version Control System ?
" Version Control System keeps track of the records changes to a set of files over time "
Why
we need Git or any other VCS ? Only to keep the code in a remote
repository as a backup ? Is VCS a waste of time ? Lets find answers for
these questions.
When we are creating individual projects we may not want to use a VCS. But VCS is very useful for team projects.
Imagine
you are working on a team project without using a VCS. Each of your
team members given individual tasks and plan is to combine those tasks
at the end. But practically it would be a very difficult. There can be
lots of redundant of codes, redundant of libraries, sometimes combining
costs lots of time and even may be unable to combine.
Imagine a scenario in which everybody can work under a same framework,
every one do there part and add to a common repository so that different
individuals can see who has committed (added the code), when it is
included, what are the changes etc. Life is so easy !
This is precisely what Version Control System capable for.
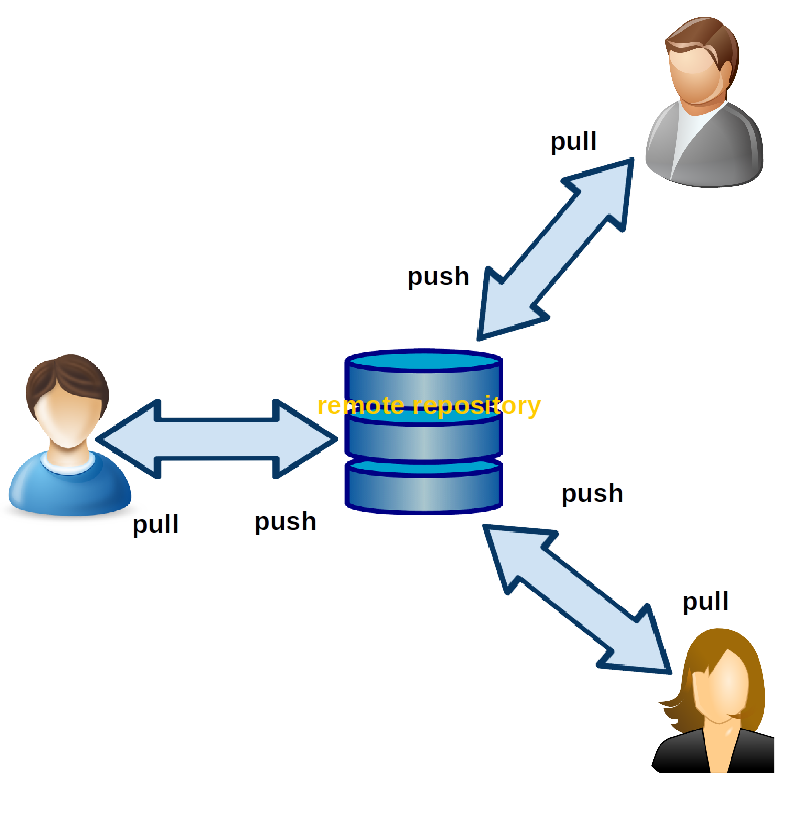
You always have a updated local repository (repository in your computer) of the remote repository (repository in VCS network) (pull). Changes you've made is first effects in your local repository. Then push(add) those changes to remote repository.
This is precisely what Version Control System capable for.
You always have a updated local repository (repository in your computer) of the remote repository (repository in VCS network) (pull). Changes you've made is first effects in your local repository. Then push(add) those changes to remote repository.
Basic git commands
git branch : show which branch you are currently working
list down branches working on. start symbol shows the current branch working on
git status : current status of your local repository (modified files)
modified file with the path is shown red color
git diff path-to-file : show what are the changes of modified file
removed line of the file is shown with red color
git reset --hard
HEAD : reset local repository
HEAD is now reset to current fix AAERESAA-19915
less .git/config : configure git configurations
git pull : update
local repository from remote repository (pull changes from remote repository to local)
git checkout –
–track path-to-branch : changes the working path
git reset – –soft
shaID : reset the state until given shaID
git add path-to-file
: stage the file (ready the file to commit)
git commit -m
“commit-message” : commit the file
git push origin
branch-name : push to remote repository
gitk : shows the git repository browser






Comments
Post a Comment